A Small Business's Guide to Cyber Insurance
UPDATED: July 1, 2024
Cyber attacks are increasing. This isn't a new statistic, and to be honest, you're probably groaning to yourself, saying "I know this." We get it, you know there are risks. But the biggest risk people don't often consider is what their business is doing to meet requirements for Cyber Insurance. Not only is it convoluted with jargon closer to building a bomb than protecting your business. But it's important jargon an we're here to help make sure you've got the right people and processes in place to meet your policy's strict requirements. Get answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about cyber insurance coverage — and its gaps.
From global brands to local small and midsized businesses (SMBs), everyday brings thousands of new cyber attacks and malicious hacks to organizations of all types. The priority for many IT directors, administrators, and consultants has shifted from preventing cyber attacks completely towards preparing for a swift recovery post-incident and minimizing subsequent damage.
Cyber insurance is a critical part of keeping a business afloat after a cyber security incident. While some cyber insurance policies have often been criticized for their ambiguity and lack of coverage, businesses can no longer deny the need for it. The debate around cyber security insurance is evolving when it comes to small to mid-sized companies. It's becoming clear that these businesses are not only more likely to be hit by cyber crime, but also less likely to recover when a security incident occurs. Centre's team of certified experts have put together some answers to frequently asked questions among SMBs surrounding the topic of cyber insurance.
5 QUESTIONS About CYBER INSURANCE (AND THEIR ANSWERS)
1) What is Cyber Insurance?
Cyber Insurance is a range of policies businesses can purchase to manage their IT risk and cover their losses in the event of a cyber incident. These insurance policies provide funds to help businesses recover from cyber attacks, significant IT disruption, or natural disasters. With the advancement of bad actors and the rapid frequency in security breaches of all sizes, the potential of experiencing IT security failures (and cost of them) is boosting the popularity of cyber security insurance in particular.
Depending on their operations, customers, and goals, different organizations will need different types of insurance policies and coverage. First-party coverage provides financial assistance to for things like hardware and software repair, while third-party coverage helps cover costs from lawsuits and regulatory fines.
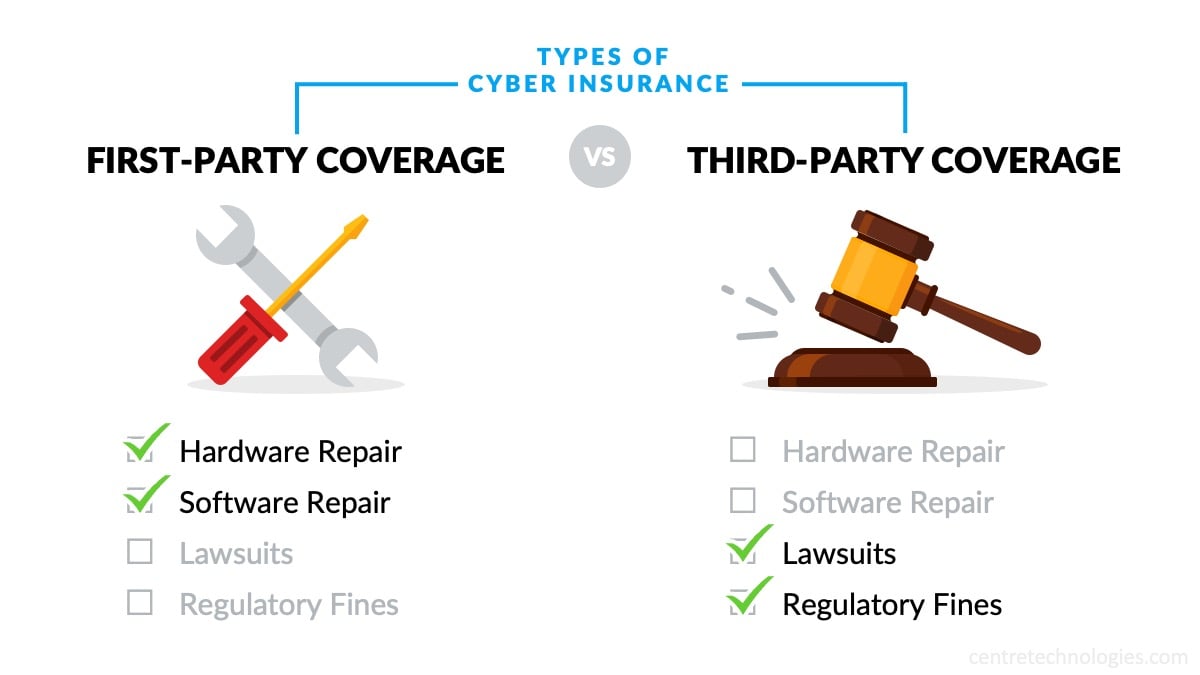
Businesses need to carefully assess what types of policies and coverage work best for them, including insurance limits, in order to choose the option that optimizes costs and liability. Additionally, organizations should consider in their financial planning and disaster recovery plan that not every cyber incident is covered by their insurance. Many insurance brokers have specific rules and conditions that must be met in order to receive insurance benefits after an incident. It's important to thoroughly vet your insurance plan and carrier, so you know exactly what to expect when a security breach occurs.
2) Do Startups Need Cybersecurity Insurance?
Startup companies are often much easier to hack than major corporations because of their little experience with cybersecurity. They typically allocate their available cash toward business growth, as opposed to data protection. With that in mind, waiting until an attack occurs could cost a startup its entire livelihood. After all, it is more of a challenge to repair consumer confidence when you don’t have the same level of consumer currency as a corporation. Designed to mitigate losses from cyber incidents, cybersecurity insurance covers breaches and restoration costs. Follow along as we think about what IT services for startups should include in order to provide genuine protection.
- What Should Be In My Business Risk Analysis?
Your startup will quickly learn that running a business puts you in line with many types of risks. Upon conducting a business risk analysis, you will be able to better understand what damages you could endure. This includes loss of earnings and productivity. Considering this, you will also be equipped to know what security software and services you need to invest in to protect your startup from these damages.
By outsourcing IT services specifically meant for startups, IT experts can thoroughly examine your issues, launch a response plan quickly, and inform those affected. Here are some of the biggest things that startups need to consider.
-
- Data breaches:
Often a result of employee negligence, data breaches that steal your business information are expensive to deal with. You would have to pay for the costs of data recovery, regulatory fines, and lawsuits. Plus, you risk never gaining back customer trust. - DDoS attacks:
This type of attack utilizes multiple compromised computer systems to push a traffic jam. They can be identified through the use of analytics tools. These locate suspicious traffic patterns that are originating from a single IP address. - Compliance regulations:
Not following legal frameworks for data storage and transmission will cause many issues for your startup. Make sure that you are implementing the measures required by the PCI Security Standards Council. - Insider threats:
If your employees don’t know the necessary protection practices, they are likely to be a weak link in your cybersecurity strategy. Your startup needs to implement awareness training. That way, employees know how to recognize social engineering attacks and how to respond to them.
- Data breaches:
- Does my startup need cybersecurity insurance?
60% of all targeted cyber attacks were experienced by small and medium businesses. This resulted in costly implications, with 60% of them losing their businesses in the following six months. By not having the proper cybersecurity measures in place, you may end up as part of that statistic.
With cybersecurity insurance, your startup receives the coverage it needs in the case of an incident. The policy is typically split into first-party and third-party coverage. As a risk-transference tool, you have protection for your business related to breaches, as well as losses that your clients suffer. Cybersecurity insurance comes in handy when you maintain a digital database of personal information and rely heavily on technology for your operations. When deciding on your provider, keep in mind the IT services your startup requires on a daily basis.
3) How Much Cyber Insurance Coverage Do I Need?
The third most common question about cyber insurance is how much coverage businesses need to purchase. The answer is not clear and will depend on each organization, especially their industry, budget, and size. Other considerations businesses should keep in mind include an obligation to their customers and suppliers, the cost of downtime, and perhaps even estimated ransom demands from ransomware.
- Obligation to customers or suppliers
Many organizations have a legal obligation to provide a product or payment to their clients or vendors. If a business experiences a breach and are not able to provide whatever it is they promised in a service level agreement, or other binding document, they may be facing a lawsuit. Businesses with many obligations to external customers or sources may want to consider purchasing greater insurance to prevent legal escalation. - The cost of downtime
Additionally, many businesses face a loss of productivity in the face of a malicious hack. Their systems and applications may be encrypted by the attackers, or they may face a loss of data which halts productivity. Organizations will want to consider whether 24 hours of downtime means a couple thousand dollars lost in production, or a couple hundred thousand, in order to determine an appropriate coverage for when a security breach happens. - Predicted damages
Lastly, we recommend businesses estimate to what capacity they might potentially be breached—and what attackers may do after that. For example, does your businesses carry a lot of consumer data that could be leaked or sold? How much ransom might an attacker demand from your company? These questions are incredibly difficult to answer, especially with precision, but they may help ballpark the amount of IT risk a cyber insurance policy would cover.
4) How Much Does Cyber Insurance Cost?
Cyber insurance works just like a typical insurance policy. Premiums depend on several factors, such as whether the business has been a victim before, what industry the business is in and its valuation or revenue, and the type of coverage being sought.
Additionally, the current IT security posture and hygiene is also used to assess the premiums and type of coverage organizations are eligible to receive. Businesses that have security tools and practices in place, such as employee awareness training, endpoint detection and response tools, as well as an incident response plan may be able to reduce their rates.
- Premiums are high, but will likely get higher
Although the actual cost varies for each organization, IT security insurance premiums are skyrocketing for businesses of almost all sizes and industries. This is no surprise given the exponential increase in attacks in almost every industry. In 2023, malware increased by over 350% and ransomware by over 400%. Additionally cyber attackers are becoming increasingly sophisticated and streamlining their process with tool-sharing platforms such as Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS). - Investing in insurance vs. investing in prevention
The cost of insurance should be carefully compared with the cost of minimizing incidents in the first place. While some types of cyber insurance has a place in every business, the amount of coverage purchased, the limits sought, and the premiums received are all related to the current security posture of the organization. Businesses with a better ability to discover and contain threats before they escalate are likely to spend less on insurance overall.
5) What Does Cyber Insurance NOT Cover?
Often, it's easier to look at what's not covered in a policy in order to identify gaps in cyber liability coverage. Different policies and types of coverage will exclude different events or incidents. That said, there are a few cases which span universally across almost all policies.
- Undervalued Assets: Like other types of insurance, cyber insurance gives quotes and coverage based on the value of assets your business is trying to protect. This is especially useful in assessing payouts for IT system damage and lost productivity. However, if a business's IT systems and productivity are undervalued during this process, the business will not recover the full value of assets and work lost due to an incident.
- Intellectual Property Theft: It is no surprise that malicious actors may commit a data breach for access to, well, data. While this may be consumer data, such as names or contact information, it may very well be trade secrets or ideations for new products, services, or strategies. Most cyber insurance policies will not cover the loss of value associated with this information being leaked and used.
- State-Sponsored Attacks: Many insurance brokers keep their policies and conditions ambiguous towards cyber attacks which are state sponsored, terrorist, or “war-like.” Attacks, like that on Colonial Pipeline, which are done by international groups and intelligence agencies, may be excluded from the scope of a policy.
- Attacks from a Former or Current Employee: In the event of an attack from a disgruntled employee, many insurance companies may point the blame on the organization, rather than an insurable IT risk.
- Revenue or Sales Lost During Downtime: While many policies may cover a loss in production, they do not directly cover any sales or revenue lost during downtime. For example, if a consumer couldn’t make a purchase on a website due to downtime, that loss in revenue would not be covered by most policies.
- Easily Preventable Attacks: Many insurance providers will look for ways to withhold benefits and avoid giving a payout. Often, they will see if they can point the blame on the organization for negligence or poor security hygiene. If a cyber attack is deemed easily preventable, it may not receive coverage.
Get Your Questions Answered
Have questions about cyber insurance? Contact Centre Technologies to learn more about cyber insurance and how to ensure that your business is equipped to maintain productivity and efficiency after an incident, picking up where cyber insurance often fails.
Be a thought leader and share:
About the Author
Creative content writer and producer for Centre Technologies. I joined Centre after 5 years in Education where I fostered my great love for making learning easier for everyone. While my background may not be in IT, I am driven to engage with others and build lasting relationships on multiple fronts. My greatest passions are helping and showing others that with commitment and a little spark, you can understand foundational concepts and grasp complex ideas no matter their application (because I get to do it every day!). I am a lifelong learner with a genuine zeal to educate, inspire, and motivate all I engage with. I value transparency and community so lean in with me—it’s a good day to start learning something new! Learn more about Emily Kirk »

 Emily Kirk
Emily Kirk